Understanding Postpartum Sexual Dysfunction and Its Effects on Female Sexual Health
Sexual dysfunction is commonly viewed as a problem that affects men, but women, especially during major life events such as pregnancy and the postpartum period, are also at risk. Postpartum sexual dysfunction is such a medical condition that affects many women after giving birth, but it is a condition that is often underreported, underdiagnosed, and undertreated. Let us examine whether women can actually suffer from sexual dysfunction, specifically postpartum sexual dysfunction, and why it is such an important part of women’s sexual health.
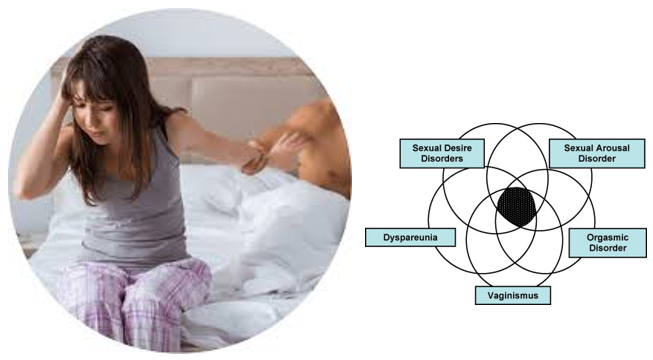
Yes, Women Can Suffer from Sexual Dysfunction
Contrary to what many people may have once believed, women’s sexual dysfunction is a real, measurable, and treatable condition. According to the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health (ISSWSH), sexual dysfunction in women can be defined as a disorder of desire, arousal, orgasm, and/or pain. These disorders are caused by a combination of biological, psychological, relational, and sociocultural factors, and pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period are major risk factors.
Best Seller
-
Cenforce 100 Mg
Best Seller$24.00 – $215.00Price range: $24.00 through $215.00Rated 4.50 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Extra Super Tadarise
ALL$48.00 – $720.00Price range: $48.00 through $720.00Rated 5.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Super Tadarise
ALL$45.00 – $446.00Price range: $45.00 through $446.00Rated 4.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Cenforce 120 Mg
Cenforce$24.00 – $299.00Price range: $24.00 through $299.00Rated 4.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Tadarise 20mg
Tadalafil$26.00 – $261.00Price range: $26.00 through $261.00Rated 4.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Tadarise 40mg
Tadalafil$28.00 – $285.00Price range: $28.00 through $285.00Rated 5.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Tadarise 60mg
Tadalafil$36.00 – $366.00Price range: $36.00 through $366.00Rated 5.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Super Vidalista 80 Mg
ALL$78.00 – $784.00Price range: $78.00 through $784.00Rated 5.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Vidalista 10 Mg
Tadalafil$20.00 – $206.00Price range: $20.00 through $206.00Rated 4.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Vidalista 2.5 Mg
Tadalafil$17.00 – $171.00Price range: $17.00 through $171.00Rated 4.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Vidalista 20 Mg
Tadalafil$24.00 – $405.00Price range: $24.00 through $405.00Rated 4.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Vidalista 5 Mg
best sellers$18.00 – $182.00Price range: $18.00 through $182.00Rated 4.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Vidalista 60 Mg
Tadalafil$35.00 – $350.00Price range: $35.00 through $350.00Rated 4.00 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Vidalista Black 80 Mg
E.D/P.A.H$56.00 – $558.00Price range: $56.00 through $558.00Rated 4.50 out of 5Shop Now This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Is Postpartum Sexual Dysfunction a serious issue?
Postpartum sexual dysfunction is the persistent problem of sexual desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, or satisfaction that occurs after childbirth. It can also include painful intercourse i.e., dyspareunia, lack of sexual interest or intimacy, or feelings of disconnection from their partner. Symptoms can begin within weeks of giving birth and may persist for months or years if untreated. Yes, Postpartum sexual dysfunction can be serious issue if not treated.
Prevalence
- Up to 80 percent of women experience some sexual problem in the first three months after giving birth.
- About 40-50 percent of women continue to experience sexual problems six months after childbirth.
- About 20 percent of women meet the criteria for female sexual dysfunction one year after childbirth.
These statistics highlight that postpartum sexual dysfunction is not an uncommon problem it is common, yet often normalized as “part of being a mother.”
Causes of Postpartum Sexual Dysfunction
- Hormonal Changes
The sudden drop in estrogen and progesterone levels just after the childbirth, further exacerbated by breastfeeding, can result in vaginal dryness, thinning of vaginal walls, reduced elasticity, and reduced sensitivity. These biological alterations directly affect arousal and pain.
- Physical Trauma
Just after giving birth pelvic area can be get damaged:
- Vaginal pain, tears or episiotomy scars may result in chronic pain.
- The recovery period from cesarean section surgery may restrict mobility and body awareness.
- Weakness or hypertonicity of pelvic floor muscles can reduce lubrication, sensation, and orgasmic function.
- Psychological Factors
Postpartum depression, anxiety, trauma during childbirth experience, body image issues, and fear of another pregnancy result in reduced libido and avoidance of sexual intercourse.
- Lifestyle and Relationship Stressors
It may lead to fatigue, lack of privacy, new responsibilities, sleep may get disturbed and changes in relationship with partner, create emotional distance this may affects adversely.
- Cultural Silence
Societal norms against open discussion of postpartum sexuality result in delayed in postpartum care that may lead to sexual dysfunction.
Impact on Female Sexual Health
Female sexual health may encompass the mere absence of disease it encompasses physical pleasure, emotional fulfillment, relational harmony, and self-esteem.
Postpartum sexual dysfunction affects all these areas:
- Impacts quality of life and their relationship.
- Increases the risk of postpartum mood Swings and Disorder.
- May result in the avoidance of future pregnancies out of fear of recurrence.
- Contributes to feelings of inadequacy or guilt or nervousness.
The failure to address postpartum sexual dysfunction simply continues the cycle of shame and isolation, which contributes to the poor overall health of women.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Healthcare professionals should assess for sexual issues during the postpartum visit using a reliable instrument such as the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI). The evaluation should include the following:
- Medical history: type of delivery, breastfeeding, and medications.
- Physical examination: pelvic floor, evidence of atrophy, and scar tissue.
- Psychological assessment: mood, body image, and relationship satisfaction.
- Partner communication: understanding of joint expectations and emotional needs.
Management Strategies
- Medications
- Topical estrogen creams, or tablets reverse vaginal atrophy and improve lubrication without any serious side effects.
- Low-dose testosterone replacement therapy may be considered safe and effective for patients under the guidance of a specialist.
- Pelvic Floor Therapy
Specialized physical therapy focuses on muscle tone, fibrosis, and pain, improving arousal pathways and dyspareunia.
- Lubricants and Moisturizers
Water-soluble or silicone lubricants reduce discomfort, while vaginal moisturizers maintain tissue integrity, both lubricants and moisturizers are very useful during this period.
- Psychosocial Care
Cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness-based therapy, or sex therapy address anxiety, body image, and intimacy phobias is required in order to treat such symptoms.
- Relationship Therapy
Couples therapy reestablishes emotional intimacy, reframes intimacy beyond intercourse, and encourages realistic expectations.
- Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes like food, beverages, alcohol may also leads to such issues.
Conclusion
Yes, Women may experience sexual dysfunction, especially in the postpartum period due to emotional, hormonal changes and physical issues. Postpartum sexual dysfunction is not embarrassing but a serious concern that needs medical attention. By looking into sexual health postpartum care, healthcare systems can support women’s prepartum experiences, decrease embarrassment, and facilitate recovery. Prioritizing female sexual health empowers women to recover physically, emotionally, and relationally from childbirth.
FAQ's
1. Can women experience sexual dysfunction?
Yes, Women Can Suffer from Sexual Dysfunction.
2. What do you mean by sexual dysfunction?
sexual dysfunction in can be defined as a disorder of desire, arousal, orgasm, and/or pain.
3. Does Postpartum leads to sexual dysfunction?
Yes, Postpartum may leads to sexual dysfunction.
4. I feel disconnected from my partner sexually is it common?
It can be due to postpartum, you need to consult a doctor.
5. Are orgasm different postpartum?
Yes, weaker, delayed or harder to reach. Pelvic floor rehab, arousal techniques can help restore sensation.